MySql 安装 使用
版权申明:本文为原创文章,转载请注明原文出处
- MySql安装 使用
- MySql官网
- yum安装官网下载页
索引
前言
- MySql安装 使用
- MySql官网
- yum安装官网下载页
官网下载 安装MySql
CentOS 安装MySql
- 在mysql官网下载repo源
- centos的 yum 源中默认是没有mysql的,所以我们需要先去官网下载mysql的repo源并安装
mysql官网下载链接:mysql repo yum 下载地址
上传 repo 源到 centos服务器
将下载的mysql80-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm上传到centos服务器的:/usr/local/mysql目录中安装yum repo文件并更新yum缓存
- 安装yum repo文件执行结果会在/etc/yum.repos.d/目录下生成两个repo文件:mysql-community.repo 和 mysql-community-source.repo
1
2
3
4# 进入文件所在文件夹
cd /usr/local/mysql
# 安装yum repo文件
rpm -ivh mysql80-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm - 更新 yum 命令
1
2yum clean all
yum makecache
- 安装yum repo文件
选择mysql的安装版本
当我们在使用yum安装mysql时,yum默认会从yum仓库中安装mysql最新的GA版本;如何选择自己的版本;
第一步: 查看mysql yum仓库中mysql版本,使用如下命令
yum repolist all | grep mysql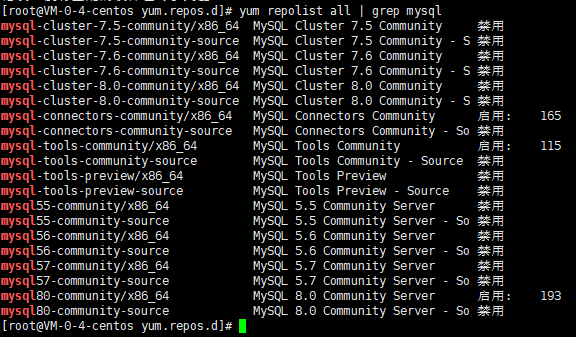
可以看到 MySQL 5.5 5.6 5.7为禁用状态 而MySQL 8.0为启用状态或者可以编辑 mysql repo文件,
cat /etc/yum.repos.d/mysql-community.repo
将相应版本下的enabled改成 1 即可
安装mysql
yum install mysql-community-server
使用 MySql
启动mysql服务 和 常用命令
//启动命令
systemctl start mysqld.service
//重启命令
systemctl restart mysqld.service
//停止命令
systemctl stop mysqld.serivce
//开启mysql开机自启动
systemctl enable mysqld.service
//关闭mysql开机自启动
systemctl disable mysqld.service
获取 mysql 初始密码
mysql在安装后会创建一个
root@locahost账户,并且把初始的密码放到了/var/log/mysqld.log文件中;1
2
3cat /var/log/mysqld.log |grep password
[root@localhost mysql]# cat /var/log/mysqld.log |grep password
2022-04-02T01:30:35.121174Z 6 [Note] [MY-010454] [Server] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: a12LlkwlDe8:r使用初始密码登录 mysql
mysql -u root -p修改初始密码
将MyNewPass4!替换成你的新密码 注意:后面的;分号一定不能少ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass4!';
配置文件
命令
1
2
3
4
5
6[root@localhost mysql]# mysql --help|grep 'my.cnf'
order of preference, my.cnf, $MYSQL_TCP_PORT,
/etc/my.cnf
/etc/mysql/my.cnf
/usr/etc/my.cnf
~/.my.cnfmysql会依次寻找配置文件 所以直接修改第一个
/etc/my.cnf就可以了
Mysql日志默认存放位置
位置
/var/log/mysqld.log也可以查看
/etc/my.cnf文件的log-error=
Mysql数据库默认存放位置
路径
/var/lib/mysql也可以查看
/etc/my.cnf文件的datadir=
登录MySql
命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15[root@localhost mysql]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password: #这里输入密码
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 9
Server version: 8.0.28 MySQL Community Server - GPL
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
查看默认端口
- 命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7mysql> show global variables like 'port';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| port | 3306 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
修改默认端口
编辑文件
/etc/my.cnf/etc/my.cnf 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32# For advice on how to change settings please see
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
# *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the
# *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you
# *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL.
[mysqld]
# 设置3306端口
port=3306 #根据自己的需要修改端口
# 设置mysql的安装目录
basedir=L:\1_mysql\mysql-8.0.19-winx64 #根据自己的文件位置修改
# 设置mysql数据库的数据的存放目录
datadir=L:\1_mysql\mysql-8.0.19-winx64\Data #根据自己的文件位置修改
# 允许最大连接数
max_connections=200
# 允许连接失败的次数。这是为了防止有人从该主机试图攻击数据库系统
max_connect_errors=10
# 服务端使用的字符集默认为UTF8
character-set-server=utf8
# 创建新表时将使用的默认存储引擎
default-storage-engine=INNODB
# 默认使用“mysql_native_password”插件认证
default_authentication_plugin=mysql_native_password
sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'
[mysql]
# 设置mysql客户端默认字符集
default-character-set=utf8
[client]
# 设置mysql客户端连接服务端时默认使用的端口
port=3306 #根据自己的需要修改端口
default-character-set=utf8
# 设置此项很危险 会无密码访问数据库
# skip-grant-tables修改端口后启动mysql时 如果报错
Job for mysqld.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status mysqld.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.而且日志
/var/log/mysqld.log里 报错[ERROR] [A] [Server] Can't start server: Bind on TCP/IP port: Permission denied [ERROR] [A] [Server] Do you already have another mysqld server running on port: 3307 ? [ERROR] [A] [Server] Aborting此问题是没关安全增强型Linux导致
修改/etc/selinux/config文件内容的SELINUX=disabledvi /etc/selinux/config修改好保存 重启服务器后 就可以启动
MySql了reboot
开启 mysql 远程服务
- 设置账号远程登录
可能你的帐号不允许从远程登陆,只能在localhost本地使用。
可以更改
mysql数据库的user表的host项,从localhost改称%使用户可以通过远程登录
执行如下命令 登录mysql数据库1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13#进入mysql
mysql -u root -p
#输入密码
#选择使用库名mysql
mysql> use mysql;
//这条命令的作用 让root用户可以在远程使用
//在user表的user列 中匹配关键字为root的项 并修改host项的值为%
mysql> update user set host='%' where user='root';
//如果改回只能本机使用 执行:
mysql> update user set host='localhost' where user='root';选择查询 来自user表中的所有项 并显示出host列 和 user列中所有的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10mysql> select host,user from user;
+-----------+------------------+
| host | user |
+-----------+------------------+
| % | root |
| localhost | mysql.infoschema |
| localhost | mysql.session |
| localhost | mysql.sys |
+-----------+------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用授权的方式
赋予任何主机访问数据的权限
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%'; //给某用户所有权限 mysql> flush privileges; //刷新如果想myuser用户使用mypassword密码从任何主机连接到mysql服务器的话。
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'%'IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';如果你想允许用户myuser从ip为192.168.1.3的主机连接到mysql服务器,并使用mypassword作为密码
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'192.168.1.3'IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
创建用户
命令:
mysql> CREATE USER 'username'@'host' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';说明:
- username:你将创建的用户名
- host:指定该用户在哪个主机上可以登陆,如果是本地用户可用localhost,如果想让该用户可以从任意远程主机登陆,可以使用通配符%
- password:该用户的登陆密码,密码可以为空,如果为空则该用户可以不需要密码登陆服务器
例子:
mysql> CREATE USER 'dog'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; mysql> CREATE USER 'pig'@'192.168.1.101_' IDENDIFIED BY '123456'; mysql> CREATE USER 'pig'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; mysql> CREATE USER 'pig'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY ''; mysql> CREATE USER 'pig'@'%';
授权
命令:
GRANT privileges ON databasename.tablename TO 'username'@'host';说明:
- privileges:用户的操作权限,如SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE等,如果要授予所的权限则使用ALL
- databasename:数据库名
- tablename:表名,如果要授予该用户对所有数据库和表的相应操作权限则可用表示,如.*
例子:
GRANT SELECT,INSERT,DELETE,CREATE ON test.user TO 'pig'@'%'; GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'pig'@'%'; GRANT ALL ON maindataplus.* TO 'pig'@'%';注意:
用以上命令授权的用户不能给其它用户授权,如果想让该用户可以授权,用以下命令:
GRANT privileges ON databasename.tablename TO 'username'@'host' WITH GRANT OPTION;
更改数据库默认数据文件路径
进入mysql
mysql -u root -p 输入mysql密码查看数据库默认路径
mysql> show global variables like '%datadir%';停止mysql
sudu systemctl stop mysqld.service拷贝数据库到新的路径 (新路径不要使用/root/路径 否则无论你如何修改都解决不了权限问题 永远报error 13 大坑)
cp -a -p /var/lib/mysql/* /mysql更改新路径的归属为mysql用户
chown -hR mysql:mysql /mysql更改新路径的权限
chmod 750 /mysql修改配置文件
datadir和socket项为新路径vi /etc/my.cnf datadir=/mysql socket=/mysql/mysql.sock重新初始化配置文件
mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --initialize --user=mysql启动mysql
sudu systemctl start mysqld.service坑
遇到的大坑就是 千万别把新路径设置在 /root下面 否则权限问题搞死你 永远启动报错 无论权限怎么给 都一样
修改默认日志文件
和 修改数据库默认路径 基本相同
修改配置文件
log-error项为新路径vi /etc/my.cnf log-error=/mysql/mysqld.log重启mysql 就可以了
sudu systemctl restart mysqld.service如果有权限问题 按 更改数据库默认数据文件路径 给权限就可以了
常用sql语句
退出mysql
mysql> quit mysql> exit查看mysql版本
mysql> select version();选择使用mysql这个库
mysql> use mysql;删除来自user表单中 user列中匹配root而且host列中还需要匹配% 的项
mysql> delete from user where User="root" and Host="%";刷新
mysql> flush privileges;
数据库工具
SQLyog 工具
- 当设置好了 远程访问mysql后可以使用SQLyog工具 来管理mysql包括用户管理 各个库的表单管理
- SQLyog管理用户:建立连接后选择mysql – 工具 – 用户管理
- 权限授予 – 新建用户 – 删除用户 – 修改密码 – 每小时查询更新连接数目最大值 – 用户连接最大值
链接
- 如果有需要删除mysql原有版本 可以参考此文章
MySql 安装 使用

